|
Optical
Specifications
Optical
Materials
Achromatic
Lenses
Spherical
Lenses
Cylindrical
Lenses
Prisms
Penta
Prisms
Corner
Cube Retroreflector
Waveplate
Beamsplitters
Filters
Coating
Cleaning
Optics
|
|
|
|
Principle
|
|
Principle
of Waveplate
Waveplates (retardation plates or phase shifters) are made
from materials which exhibit birefringence. The velocities
of the extraordinary and ordinary rays through the birefringent
materials vary inversely with their refractive indices. The
difference in velocities gives rise to a phase difference
when the two beams recombine. In the case of an incident linearly
polarized beam this is given by a
= 2p *
d(ne-no)/l
(a -
phase difference; d - thickness of waveplate; ne,
no - refractive indices of extraordinary and ordinary
rays respectively; l-wavelength).
At any specific wavelength the phase difference is governed
by the thickness of the retarder.
|
 |
|
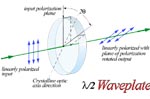
Half
Waveplate
The thickness of a half waveplate is such that the phase difference
is 1/2-wavelength (l/2,
true-zero order) or certain multiple of 1/2-wavelength [(2n+1)/l/2,
multiple
order].
A linearly polarized beam incident on a half waveplate emerges
as a linearly polarized beam but rotates such that its angle
to the optical axis is twice that of the incident beam. Therefore,
half waveplates can be used as continuously adjustable polarization
rotators. Half waveplates are used in rotating the plane of
polarization, electro-optic modulation and as a variable ratio
beamsplitter when used in conjunction with a polarization
cube.
|
 |
|
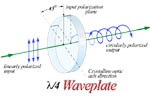
l/4
Half Waveplate
The thickness of a half waveplate is such that the phase difference
is 1/4-wavelength (l/4,
true-zero order) or certain multiple of 1/4-wavelength [(2n+1)/l/4,
multiple
order].
A linearly polarized beam incident on a half waveplate emerges
as a linearly polarized beam but rotates such that its angle
to the optical axis is twice that of the incident beam. Therefore,
half waveplates can be used as continuously adjustable polarization
rotators. Half waveplates are used in rotating the plane of
polarization, electro-optic modulation and as a variable ratio
beamsplitter when used in conjunction with a polarization
cube.
|
 |
|

