| Laser |
An
acronym for light amplification by stimulated emission
of radiation. A laser is a cavity, with mirrors at the
ends, filled with material such as crystal, glass, liquid,
gas or dye. A device which produces an intense beam
of light with the unique properties of coherence, collimation
and monochrome. |
| Lenses |
A
curved piece of optically transparent material which
depending on its shape, is used to either converge or
diverge light. |
| Longitudinal
Mode |
Determines
the wavelength bandwidth produced by a given laser system
controlled by the distance between the two mirrors of
the laser cavity. Individual longitudinal modes are
produced by standing waves within a laser cavity.
|
| M2 |
M2
is a beam quality index that measures the difference
between an actual beam and the Gaussian beam.
|
| Mode |
A
term used to describe how the power of a laser beam
is geometrically distributed across the cross section
of the beam. Also used to describe the operating mode
of a laser such as continuous or pulsed. |
| Modulation |
The
ability to superimpose an external signal on the output
beam of the laser as a control. |
| Nd:YVO4
Laser |
A
solid-state laser of Neodymium: Yttrium Vanadium Oxide,
similar to Nd:YAG but with the characteristics of higher
gain and shorter upper state lifetime.
|
| Optical
Density |
Protection
factor provided by a filter (such as used in eyewear,
viewing windows, etc.) at a specific wavelength. Each
unit of OD represents a 10x increase in protection.
|
| Output
Power |
The
energy per second measured in watts emitted from the
laser in the form of coherent light. |
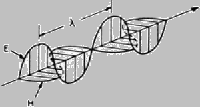
| Polarization |
Restriction
of the vibrations of the electromagnetic field to a
single plane, rather than the innumerable planes rotating
about the vector axis. This prevents optical losses
at interfaces between the lasing medium and optical
elements. Various forms of polarization include random,
linear (plane), vertical, horizontal, elliptical, and
circular. Of two polarization components (so-called),
S and P, the P component has zero losses at Brewster¡¯s
angle. ¦Ë = wavelength E = electric vector H = magnetic
vector. |
|
|
| Prism |
A
transparent optical element having at least two polished
plane faces inclined relative to each other, from which
light is reflected or through which light is refracted. |
| Pumping |
The
process to raise atoms from lower level to upper level
is called pumping.
Q: The energy-storing efficiency of a laser resonator.
The higher the "Q," the less energy loss.
|
