| What
is a Laser
Laser
Components
Time Modes of Operation
Laser
Modes
Longitude
Modes
Tramsverse
Modes
M2
Factor
Wavelength
Chart
DPSS
Laser
Infrared
Filter
Apparent
Brightness
Laser
Safety
Laser
Classification
Lasers
Glossary 1
Lasers
Glossary 2
|
|
Time
Modes of Operation
|
| The
different time modes of operation of a laser are distinguished
by the rate at which energy is delivered. |
|
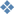
|
Continuous
wave (CW) lasers operate with a stable average
beam power. In most higher power systems, one is able
to adjust the power. In low power gas lasers, such as
HeNe, the power level is fixed by design and performance
usually degrades with long-term use. |
|

|
Single
pulsed (normal mode) lasers generally have
pulse durations of a few hundred microseconds to a few
milliseconds. This mode of operation is sometimes referred
to as long pulse or normal mode |
|

|
Single
pulsed Q-switched
lasers are the result of an intracavity delay
(Q-switch cell) which allows the laser media to store
a maximum of potential energy. Then, under optimum gain
conditions, emission occurs in single pulses; typically
of 10-8 second time domain. These pulses will
have high peak powers often in the range from 106
to 109 watts peak. |
|

|
Repetitively pulsed or scanning
lasers generally involve the operation of pulsed
laser performance operating at a fixed (or variable) pulse
rate which may range from a few pulses per second to as
high as 20,000 pulses per second. The direction of a CW
laser can be scanned rapidly using optical scanning systems
to produce the equivalent of a repetitively pulsed output
at a given location. |

|
Mode-locked
lasers
operate as a result of the resonant modes of the optical
cavity which can affect the characteristics of the output
beam. When the phases of different frequency modes are
synchronized, i.e., "locked together," the different
modes will interfere with one another to generate a beat
effect. The result is a laser output which is observed
as regularly spaced pulsations. Lasers operating in this
mode-locked fashion, usually produce a train of regularly
spaced pulses, each having a duration of 10-15
(femto) to 10-12 (pico) sec. A mode-locked
laser can deliver extremely high peak powers than the
same laser operating in the Q-switched mode. These pulses
will have enormous peak powers often in the range of 1012
(tera) watts peak. |
|
|
